Intel notes¶
Intel/Altera¶
Note
CYC1000
C10LP-RefKit
DE0
de0nano
Loading a bitstream¶
SVF and RBF files are supported.
sof to svf generation:
quartus_cpf -c -q 12.0MHz -g 3.3 -n p project_name.sof project_name.svf
sof to rbf generation:
quartus_cpf --option=bitstream_compression=off -c project_name.sof project_name.rbf
Warning
As mentioned in cyclone handbooks, real-time decompression is not supported by FPGA in JTAG mode.
Keep in mind to disable this option.
You can have Quartus automatically generate SVF and RBF files by adding these lines to the qsf file, or include them in a tcl file in FuseSoC
set_global_assignment -name ON_CHIP_BITSTREAM_DECOMPRESSION OFF
set_global_assignment -name GENERATE_RBF_FILE ON
set_global_assignment -name GENERATE_SVF_FILE ON
file load:
openFPGALoader -b boardname project_name.svf
# or
openFPGALoader -b boardname project_name.rbf
with boardname = de0, cyc1000, c10lp-refkit, de0nano, de0nanoSoc or qmtechCycloneV.
SPI flash¶
RPD and RBF are supported. POF is only supported for MAX10 (internal flash).
pof to rpd:
quartus_cpf -c project_name.pof project_name.rpd
sof to rpd:
# CYC1000
quartus_cpf -o auto_create_rpd=on -c -d EPCQ16A -s 10CL025YU256C8G project_name.svf project_name.jic
# C10LP-RefKit
quartus_cpf -o auto_create_rpd=on -c -d EPCQ16A -s 10CL055YU484C8G project_name.svf project_name.jic
file load:
openFPGALoader -b boardname -r project_name_auto.rpd
# or
openFPGALoader -b boardname -r project_name.rbf
with boardname = cyc1000, c10lp-refkit.
MAX10: FPGA Programming Guide¶
Supported Boards:
step-max10_v1
analogMax
Supported File Types:
svfpofbin(arbitrary binary files)
Internal Flash Organization¶
The internal flash is divided into five sections:
UFM1andUFM0for user dataCFM2,CFM1, andCFM0for storing one or two bitstreams
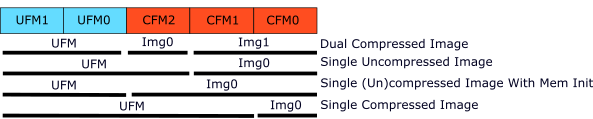
Flash usage depends on the configuration mode. In all modes:
CFM0is used to store a bitstreamUFM0andUFM1are available for user dataThe remaining
CFMxsections (CFM1,CFM2) can be used for additional bitstreams or user data
Using svf¶
This method is the simplest (and slowest) way to load or write a bitstream.
Note
This method is required to load a bitstream into SRAM.
openFPGALoader [-b boardname] -c cablename the_svf_file.svf
Parameters:
boardname: One of the boards supported byopenFPGALoader(optional).cablename: One of the supported cables (see--list-cables).
Using pof¶
To write a bitstream into the internal flash, using a pof file is the
fastest approach.
openFPGALoader [-b boardname] [--flash-sector] -c cablename the_pof_file.pof
Parameters:
boardname: A board supported byopenFPGALoader(optional).cablename: One of the supported cables (see--list-cables).--flash-sector: Optional. Comma-separated list of sectors to update. If omitted, the entire flash is erased and reprogrammed.
Accepted Flash Sectors:
UFM0,UFM1: User Flash Memory sections.CFM0,CFM1,CFM2: Configuration Flash Memory sectors.
Example:
openFPGALoader -c usb-blaster --flash-sector UFM1,CFM0,CFM2 the_pof_file.pof
This command updates UFM1, CFM0, and CFM2, leaving all other
sectors unchanged.
Using an arbitrary binary file¶
Unlike Altera Quartus, it supports any binary format without limitations
(not limited to a .bin).
With this feature, it’s not required to provides the file at gateware build
time: it may be updated at any time without gateware modification/rebuild.
Note
This approach is useful to updates, for example, a softcore CPU firmware.
Basic usage:
openFPGALoader [-b boardname] -c cablename [--offset $OFFSET] the_bin_file.bin
boardname: a boards supported byopenFPGALoader(optional).cablename: One of the supported cables (see--list-cables).$OFFSET: To start writing$OFFSETbytes after User Flash memory start address (optional, default: 0x00).
This command erases and writes the contents of the_bin_file.bin into
UFM1 and UFM0. If --offset is specified, the binary content is
written starting from that offset.
Depending on the max10 configuration mode (see picture), it’s possible to extend User Flash Memory area by using CFM2 and CFM1. This is not the default behavior and user must explictly change this by using –flash-sector argument:
--flash-sector UFMxor--flash-sector CFMy(with x= 1 or 0 and y = 2 or 1) to specify only one sector--flash-sector UFM1,UFM0is equivalent to the default behavior--flash-sector UFM1,CFM2to erase and updateUFM1,UFM0andCFM2(equivalent to--flash-sector UFM1,UFM0,CFM2)
Intel/Altera (Old Boards)¶
Note
Cyclone II (FPGA) (Tested OK: EP2C5T144C8N)
Max II (CPLD) (Tested OK: EPM240T100C5N)
Loading a Serial Vector Format (.svf)¶
SVF files are supported.
To load the file:
openFPGALoader -c usb-blaster project_name.svf